Introduction — How to Invest in Stocks

Learning how to invest in stocks is one of the most important financial skills in 2025. For beginners in the USA, UK, Canada, and Australia, understanding how to invest in stocks can open the door to long‑term wealth creation, passive income, and financial independence. Unlike saving money in a bank account, stocks give you ownership in real companies, meaning you share in their growth, profits, and sometimes dividends.
Many people wonder how to invest in stocks for beginners without risking too much. The truth is, the journey of how to invest in stocks starts with education and strategy. You don’t need millions to begin; even small amounts can grow significantly over time if invested wisely. By learning how to invest in stocks step by step, you can avoid common mistakes and build a portfolio that matches your goals.
In this guide, we’ll break down how to invest in stocks into clear, actionable sections. You’ll learn what stocks are, how to set investment goals, how to open a brokerage account, and which strategies work best for beginners. Whether you’re asking how to invest in stocks online, how to invest in stocks long term, or how to invest in dividend stocks, this post will serve as your complete roadmap.
The importance of knowing how to invest in stocks today cannot be overstated. Global markets are more accessible than ever, with online brokers offering commission‑free trades and mobile apps making investing simple. But accessibility doesn’t replace knowledge. If you don’t understand how to invest in stocks safely, you risk losing money to volatility, poor decisions, or emotional trading.
By the end of this article, you’ll not only know how to invest in stocks but also how to do it strategically, minimizing risks while maximizing rewards. This introduction is the first step in your journey — let’s dive deeper into the fundamentals of how to invest in stocks and build the foundation for your financial future.
Understanding Stocks — How to Invest in Stocks
Before you can truly master how to invest in stocks, you need to understand what a stock actually represents. A stock is a share/part in a company that you own. When you buy a stock, you’re buying a piece of that business, entitling you to a portion of its profits and, in some cases, voting rights. This is the foundation of learning how to invest in stocks for beginners — knowing what you own and why it matters.
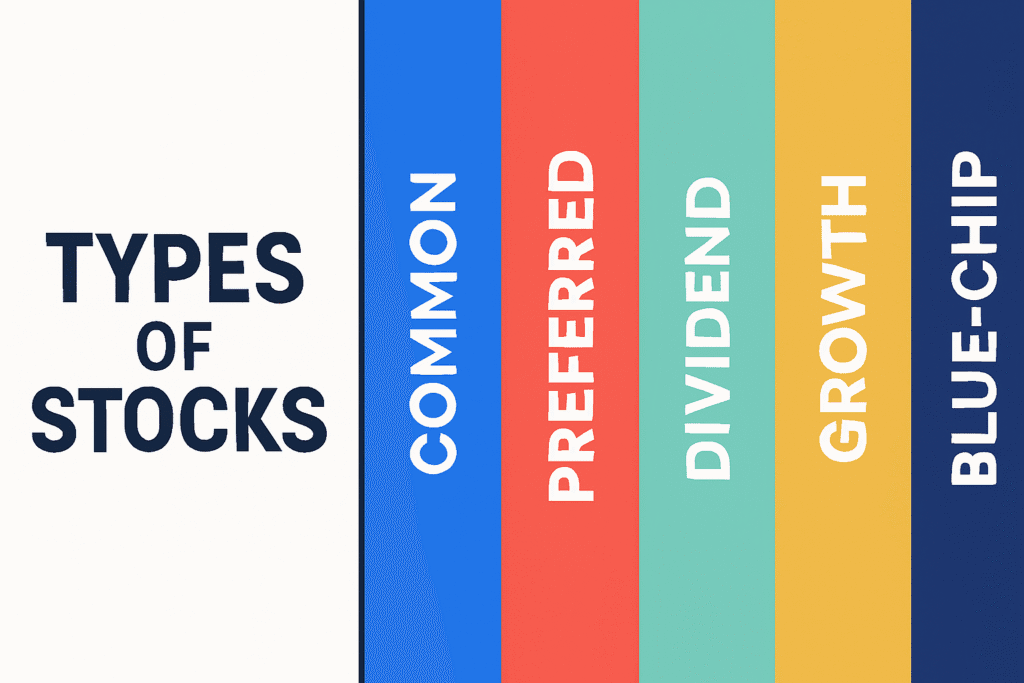
Types of Stocks
- Common Stock: The most widely held type. It gives shareholders potential dividends and voting rights. Anyone asking how to invest in stocks will almost always start here.
- Preferred Stock: Offers fixed dividends but usually no voting rights. Investors exploring how to invest in stocks for income often consider preferred shares.
- Blue‑Chip Stocks: Large, stable companies like Johnson & Johnson or Microsoft. Beginners often ask how to invest in stocks safely, and blue‑chips are a common answer.
- Growth Stocks: Companies reinvesting profits to expand rapidly. If you’re wondering how to invest in stocks for long‑term growth, these are key.
- Dividend Stocks: Firms that share profits regularly with shareholders. Anyone learning how to invest in stocks for passive income should study these.
Why Stocks Matter
Understanding stocks is crucial because they are the building blocks of wealth creation. If you’re asking how to invest in stocks online, you’ll quickly realize that stocks are the most accessible investment vehicle today. They allow you to participate in the success of global companies without needing to start a business yourself.
Example
Suppose you buy 10 shares of Apple. You now own a fraction of Apple Inc. If Apple grows, your shares increase in value. If Apple pays dividends, you receive a portion of its profits. This simple example illustrates why learning how to invest in stocks is the gateway to financial independence.
Key Takeaway
Before diving into brokers, strategies, or risks, you must grasp the basics of stocks. Without this foundation, you can’t truly understand how to invest in stocks effectively.
Setting Investment Goals — How to Invest in Stocks
One of the most overlooked steps in learning how to invest in stocks is defining your investment goals. Without clear objectives, even the best strategies can fail. Beginners often ask how to invest in stocks for beginners without losing money, but the answer depends on what they want to achieve.
Short‑Term Goals
If you’re wondering how to invest in stocks for short‑term needs — like saving for a car, vacation, or emergency fund — you’ll need safer, more liquid investments. Stocks can be volatile, so short‑term investors should focus on stable companies or ETFs.
Long‑Term Goals
Most people asking how to invest in stocks long term are thinking about retirement or wealth building. Long‑term investors can tolerate market ups and downs because they have time to recover. This is where strategies like buy and hold or dollar‑cost averaging shine.

Risk Tolerance
Understanding risk tolerance is essential when deciding how to invest in stocks.
- Conservative investors may prefer dividend stocks or index funds.
- Moderate investors balance growth stocks with ETFs.
- Aggressive investors chase high‑growth companies, accepting volatility.
Example
Imagine two investors asking how to invest in stocks:
- Sarah wants to retire in 30 years. She invests in diversified ETFs and dividend stocks.
- John wants quick profits. He invests in volatile tech stocks.
Both are learning how to invest in stocks, but their goals shape completely different strategies.
Key Takeaway
Defining goals is the foundation of how to invest in stocks effectively. Without knowing whether you’re investing for short‑term gains or long‑term wealth, you risk making emotional decisions that hurt your portfolio.
Opening a Brokerage Account — How to Invest in Stocks
A critical step in learning how to invest in stocks is opening a brokerage account. Without a broker, you cannot buy or sell shares in the stock market. Beginners often ask how to invest in stocks online, and the answer almost always begins with choosing the right brokerage platform.
What is a Brokerage Account?
A brokerage account is an investment account that allows you to purchase stocks, ETFs, mutual funds, and other securities. When you’re figuring out how to invest in stocks for beginners, this account acts as your gateway to the market. Before opening your first trading account, explore our detailed guide on the 10 Best Online Brokers for Beginners in USA, UK, Canada & Australia (2025) to find the platform that best fits your needs.
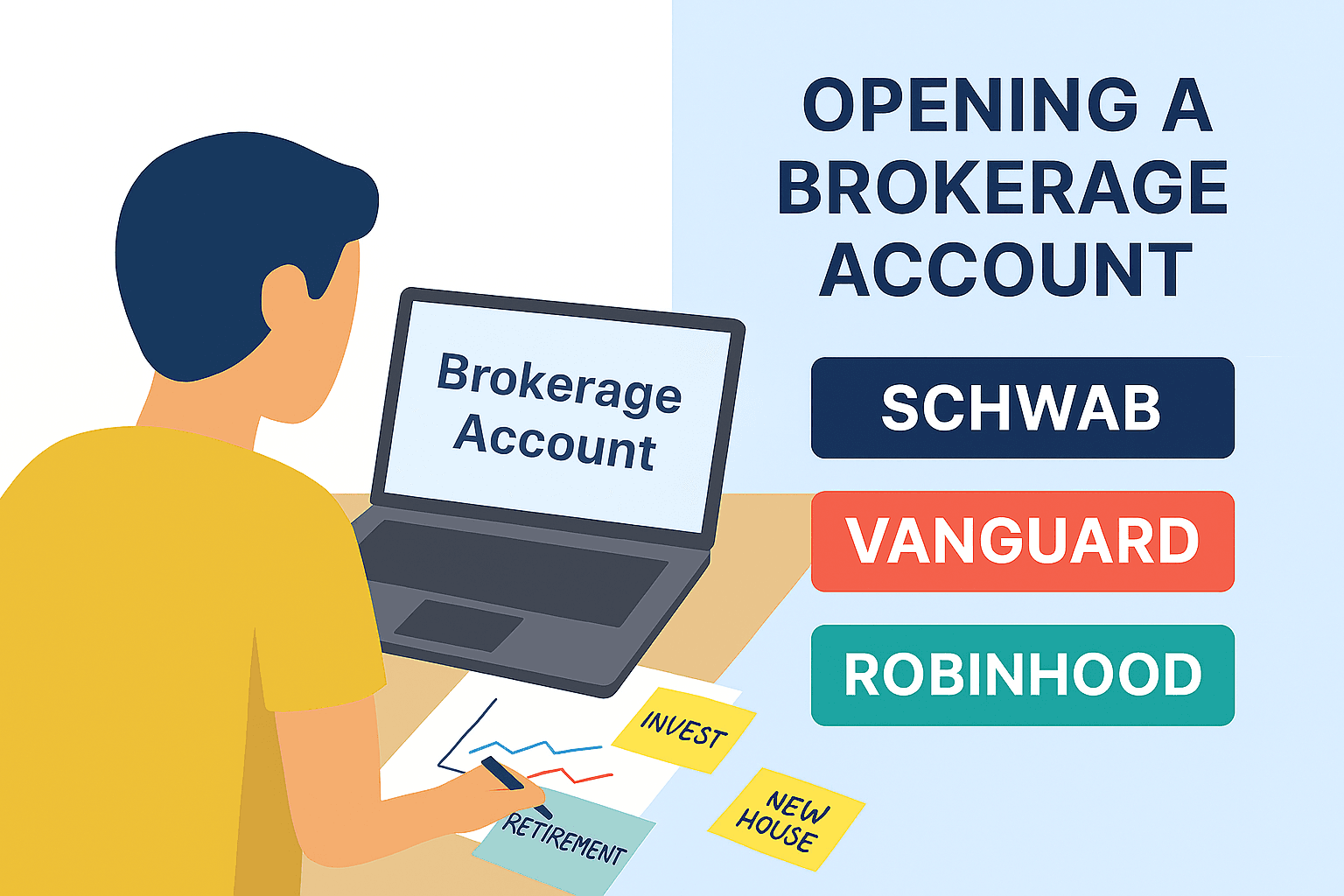
Popular Brokers for Beginners
- Vanguard: Known for low‑cost index funds and ETFs. Ideal for those asking how to invest in stocks long term.
- Charles Schwab: Beginner‑friendly, with strong customer support and educational resources. Great for anyone learning how to invest in stocks safely.
- Fidelity: Offers advanced research tools and retirement accounts. Perfect for investors exploring how to invest in stocks for retirement.
- Robinhood: Mobile‑first, commission‑free trading. Popular among younger investors asking how to invest in stocks with little money.
Steps to Open a Brokerage Account
- Choose a Broker: Decide which platform matches your goals.
- Provide Identification: Brokers require ID verification to comply with regulations.
- Fund Your Account: Transfer money from your bank.
- Start Trading: Once funded, you can begin practicing how to invest in stocks.
Example
Imagine you’re in Canada and want to learn how to invest in stocks online. You open a Schwab account, deposit $500, and buy shares of SPDR S&P 500 ETF. You’ve just taken your first step in mastering how to invest in stocks.
Key Takeaway
Opening a brokerage account is the bridge between theory and practice. Without it, you cannot apply the strategies you’ll learn in later sections. If you’re serious about learning how to invest in stocks, this step is non‑negotiable.
Researching Stocks — How to Invest in Stocks
Once you’ve opened a brokerage account, the next step in learning how to invest in stocks is research. Buying stocks blindly is risky; successful investors take time to study companies, industries, and market trends. Beginners often ask how to invest in stocks safely, and the answer lies in proper research.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis focuses on the financial health of a company. If you’re asking how to invest in stocks for beginners, this is where you start.
- Earnings per Share (EPS): Shows profitability.
- Price‑to‑Earnings Ratio (P/E): Compares stock price to earnings.
- Revenue Growth: Indicates whether the company is expanding.
- Dividend History: Important for those learning how to invest in dividend stocks.
👉 Example: If Johnson & Johnson consistently grows earnings and pays dividends, it’s a strong candidate for anyone exploring how to invest in stocks long term.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis studies price charts and patterns. Investors asking how to invest in stocks online often use these tools to time their trades.
- Moving Averages: Smooth out price trends.
- Support and Resistance Levels: Show where prices tend to bounce or stall.
- Trading Volume: Reveals investor interest.
👉 Example: If Apple’s stock breaks above a resistance level with high volume, traders may see it as a buying signal while practicing.
Research Tools
- Yahoo Finance and Google Finance for quick data.
- Brokerage Platforms like Schwab or Fidelity for in‑depth reports.
- Market News Sites for updates on earnings, mergers, or regulations.
Why Research Matters
Without research, you’re gambling. Anyone asking how to invest in stocks effectively must understand that knowledge reduces risk. Research helps you avoid weak companies and focus on businesses with strong fundamentals and growth potential.
Key Takeaway
Research is the backbone of investing in stocks. Whether you prefer fundamental analysis, technical analysis, or a mix of both, informed decisions are always better than emotional ones.
Building a Portfolio — How to Invest in Stocks
A major part of learning how to invest in stocks is understanding portfolio construction. A portfolio is simply the collection of investments you own. Beginners often ask about investing in stocks safely, and the answer almost always includes diversification.
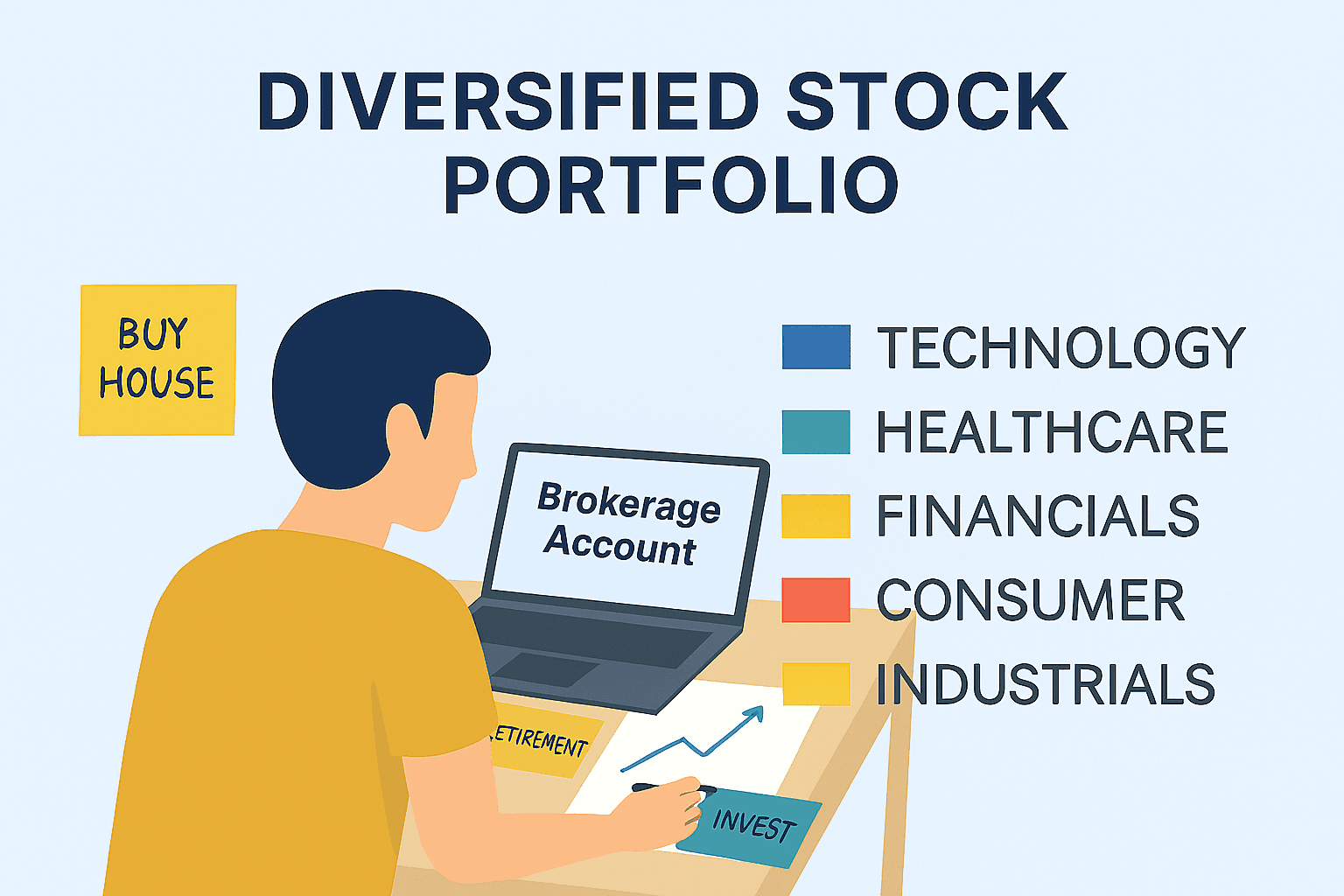
Diversification
Diversification means spreading your money across different companies, sectors, and asset types. If you’re asking how to invest in stocks for beginners, diversification protects you from losing everything if one company fails.
- By Sector: Tech, healthcare, finance, energy.
- By Geography: USA, UK, Canada, Australia, emerging markets.
- By Asset Type: Individual stocks, ETFs, index funds.
👉 Example: If you’re learning invest in stocks long term, you might hold Apple (tech), Johnson & Johnson (healthcare), and SPDR S&P 500 ETF (broad market).
Balancing Risk and Reward
When deciding how to invest, balance is key.
- High‑Risk Assets: Growth stocks with big potential but volatility.
- Low‑Risk Assets: Blue‑chip dividend stocks or ETFs.
- Medium‑Risk Assets: Mid‑cap companies with steady growth.
This mix ensures that even if one part of your portfolio struggles, others can stabilize it.
Portfolio Strategies
- Core and Satellite: Use ETFs as the “core” and add individual stocks as “satellites.”
- Dividend Focus: Build around companies that pay consistent dividends.
- Growth Focus: Target companies reinvesting profits for expansion.
Anyone asking how to invest effectively should align their portfolio strategy with their goals and risk tolerance.
Example Portfolio
Imagine you’re in the UK and want to learn how to invest in stocks online. Your portfolio might look like this:
- 50% SPDR S&P 500 ETF (broad exposure)
- 20% Johnson & Johnson (dividend stability)
- 20% Apple (growth potential)
- 10% Vanguard Emerging Markets ETF (global diversification)
This mix shows how different assets can work together to achieve balance.
Key Takeaway
Building a portfolio is the practical side of investing in stocks. It’s not just about picking one company; it’s about creating a collection of investments that work together to achieve your financial goals.
Strategies for Beginners — How to Invest in Stocks
When beginners ask how to invest in stocks, the most important step is choosing the right strategy. Strategies provide structure, reduce emotional decision‑making, and help investors stay consistent. Whether you’re asking investing in stocks for beginners, investing in stocks long term, or investing in dividend stocks, these approaches form the foundation of smart investing.
Buy and Hold
The buy‑and‑hold strategy is one of the simplest ways to learn to invest in stocks. You purchase shares in strong companies or ETFs and hold them for years, ignoring short‑term market fluctuations.
- Why it works: Markets tend to rise over time.
- Example: Buying shares of Microsoft and holding them for 10+ years.
- Best for: Investors asking about investing in stocks for retirement.
Dollar‑Cost Averaging (DCA)
Dollar‑cost averaging is a powerful method for anyone learning to invest in stocks safely. Instead of investing a lump sum, you invest a fixed amount regularly (weekly, monthly), regardless of price.
- Why it works: It reduces the risk of buying at the wrong time.
- Example: Investing $200 every month into the SPDR S&P 500 ETF.
- Best for: Beginners asking how to invest in stocks with little money.
Dividend Investing
Dividend investing is ideal for those exploring investing in stocks for passive income. You buy companies that pay regular dividends, creating a steady cash flow.
- Why it works: Dividends provide income even if stock prices fluctuate.
- Example: Buying Johnson & Johnson or Coca‑Cola for consistent payouts.
- Best for: Investors asking to invest in stocks for income.
Growth Investing
Growth investing focuses on companies reinvesting profits to expand rapidly. Anyone asking how to invest in stocks for beginners with higher risk tolerance may consider this.
- Why it works: Potential for high returns if the company succeeds.
- Example: Investing in Tesla or emerging tech firms.
- Best for: Aggressive investors asking to invest in stocks long term.
Value Investing
Value investing is about finding undervalued companies trading below their intrinsic worth. Beginners often ask how to invest in stocks wisely, and value investing is a disciplined approach.
- Why it works: Buying strong companies at a discount increases long‑term gains.
- Example: Purchasing stocks with low P/E ratios compared to industry averages.
- Best for: Investors asking to invest in stocks with minimal risk.
Key Takeaway
Strategies are the backbone of investing in stocks. Whether you choose buy‑and‑hold, dollar‑cost averaging, dividend investing, growth investing, or value investing, the key is consistency. Beginners should start small, stay disciplined, and avoid emotional trading.
Risks to Consider — How to Invest in Stocks
Anyone asking how to invest in stocks must understand that risk is part of the process. Stocks can generate wealth, but they can also lose value quickly. Beginners often ask investing in stocks safely, and the answer lies in recognizing and managing these risks.
Market Volatility
Stock prices fluctuate daily due to news, earnings reports, and global events. If you’re learning how to invest in stocks for beginners, expect ups and downs.
- Example: A company’s share price may drop 10% in a single day after poor earnings.
- Tip: Long‑term investors asking to invest in stocks effectively should ignore short‑term noise and focus on fundamentals.
Company Risk
Individual companies can fail due to poor management, scandals, or competition. Anyone exploring how to invest in stocks online must research before buying.
- Example: A once‑popular retailer may collapse if it fails to adapt to e‑commerce.
- Tip: Diversification reduces this risk for those asking who invest in stocks wisely.
Economic and Political Risk
Global recessions, inflation, or political instability can impact markets. Beginners asking how to invest in stocks long term must prepare for downturns.
- Example: Rising interest rates often reduce stock valuations.
- Tip: Investors should balance portfolios with defensive sectors like healthcare or utilities.
Emotional Investing
Fear and greed are the biggest enemies of anyone learning how to invest in stocks.
- Fear: Selling too early during a downturn.
- Greed: Buying risky stocks hoping for quick profits.
- Tip: Stick to your strategy. Emotional decisions making often lead to loss.
Liquidity Risk
Some stocks are thinly traded, meaning they’re hard to sell quickly. Beginners asking about investing in stocks safely should avoid illiquid companies.
Key Takeaway
Understanding risks is essential in how to invest in stocks. Market volatility, company failures, global events, and emotional investing can all impact your portfolio. The best way to manage these risks is through diversification, research, and discipline.
Conclusion + Call to Action — How to Invest in Stocks
By now, you’ve learned the essentials of how to invest in stocks — from understanding what stocks are, setting clear investment goals, opening a brokerage account, researching companies, building a diversified portfolio, and applying beginner‑friendly strategies, to recognizing the risks involved. Each step is critical, and together they form a complete roadmap for anyone asking to invest in stocks for beginners.
The journey of learning how to invest in stocks is not about quick wins; it’s about building long‑term wealth and financial independence. Whether you’re in the USA, UK, Canada, or Australia, the principles remain the same: stay consistent, diversify, and avoid emotional decisions. If you’re wondering to invest in stocks safely, remember that discipline and research are your best allies.
Investors often ask investing in stocks long term versus investing in stocks for short‑term gains. The truth is long‑term strategies like buy‑and‑hold or dollar‑cost averaging tend to outperform short‑term speculation. If you’re focused on passive income, you can also explore how to invest in dividend stocks, which provide regular payouts alongside growth.
Final Thoughts
Learning how to invest in stocks is a lifelong skill. Markets will rise and fall, but with the right knowledge, you can navigate volatility and achieve your financial goals. Start small, stay consistent, and keep expanding your portfolio as your confidence grows.
Call to Action
If you found this guide on how to invest in stocks helpful, explore our detailed post on dividend investing to discover how dividends can provide steady income alongside growth. Together, these strategies will help you master not just to invest in stocks, but also how to build a portfolio that works for you in 2025 and beyond.


Pingback: Common vs Preferred Stocks: Which 1 Should Beginners Choose? - RevoValue – Smart Finance Insights
Pingback: Best AI Budgeting Apps in 2025: Smart Tools for Saving & Investing - RevoValue – Smart Finance Insights
Pingback: 10 Best Online Brokers for Beginners in USA, UK, Canada & Australia (2025 Guide) - RevoValue – Smart Finance Insights
Pingback: Best Online Payment Apps in USA 2025 – Secure, Fast & Trusted Options
Pingback: 10 Best AI Powered Investing Apps for Beginners with Mobile Wallets in USA, UK, Canada, Australia (2025)
Pingback: Top 10 Global Investment Trends in 2026: Smart Strategies for Long‑Term Growth - RevoValue